
The human heart beats 60 to 100 times a minute, more than 86,000 times a day, 35 million times a year. A single beat pushes about 6 tablespoons of blood through the body.
An organ that works that hard is bound to fail, says Dr. Billy Cohn, a heart surgeon at the Texas Heart Institute. And he’s right. Heart failure is the leading cause of death in men and women, killing more than 600,000 Americans every year.
For a lucky few, a heart transplant will add an average of 10 years to their lives. For others, technology that assists a failing heart — called “bridge-to-transplant” devices — will keep them alive as they wait for a donor heart.
Unfortunately, more often than not, the new heart doesn’t arrive in time.
That’s why Cohn and his mentor — veteran heart surgeon Dr. O.H “Bud” Frazier — are working to develop a long-term, artificial replacement for the failing human heart. Unlike existing short-term devices that emulate the beating organ, the new machine would propel blood through the body at a steady pace so that its recipients will have no heartbeat at all.
The concept of a pulseless heart is difficult to fathom. Cohn often compares it to the development of the airplane propeller. When people started to develop flying machines, he says, they first tried to emulate the way birds fly — by flapping the wings aggressively.
“It wasn’t until they decided, ‘We can’t do this the way Mother Nature did,’ and came up with the rapidly spinning propeller that the Wright Brothers were able to fly,” Cohn says.
The idea of an artificial heart goes back decades.
Frazier began medical school in what he describes as “the Kennedy Era.”
“We were going to the moon; we were going to achieve world peace,” and Frazier wanted to develop the first artificial heart. In 1968, he left for Vietnam as a flight surgeon. Thirteen months later, his helicopter was shot down, and he nearly died.
“That experience convinced me I should stick to something more meaningful for the rest of my life.”
That he did. The veteran surgeon, inventor and researcher has devoted the last half century to developing technologies to fix or replace the human heart, the most notable of which is the newest generation of continuous flow Left Ventricular Assist Devices, known as LVADs.
Modeled after an Archimedes Screw, a machine that raises water to fill irrigation ditches, the continuous flow LVAD is a pump that helps failing hearts push additional blood through the body with a rapidly spinning impeller.
Today, the continuous flow LVAD has been implanted in 20,000 people worldwide, including former Vice President Dick Cheney before he received a heart transplant nearly two years later.
In some cases, the LVAD’s turbine has essentially taken over the pumping process entirely from the biological heart. In these instances, the implant recipient barely has any pulse at all.
Observing what happened in these patients led Frazier to one compelling question: If the LVAD can take
over for a weakened heart, could it replace the organ entirely?
In 2004, Frazier asked Cohn to collaborate on a new research project. Cohn’s interest in heart surgery dates back to when he was a young boy reading articles about world-renowned heart surgeons Dr. Michael E. Debakey and Dr. Denton Cooley, who developed and played a role in the transplant of the first artificial heart in a human in 1969.
Now the holder of some 70-odd U.S. patents, Cohn says his work with Frazier to build an artificial heart is the most ambitious project of his career.
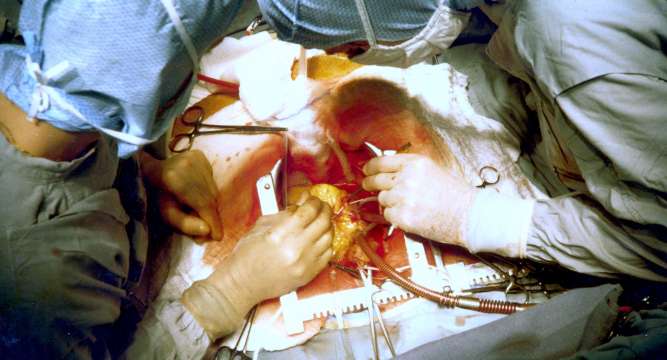
The surgeons set out to combine two LVADs to replicate the functions of the heart’s right and left ventricles. Using two commercially available LVAD turbines, Frazier and Cohn combined the devices with plastics and other material used for implants: hernia mesh, Dacron cardiovascular patches and medical silicone. Everything met FDA standards, but Cohn describes the final product as “rather kludged together.”
The surgeons tested their invention by installing it in around 70 calves. All of the cows produced a flat line on an EKG, which measures heart electrical activity, yet they stood, ate and walked around, paying seemingly no notice to a small technicality: They had no heartbeat.
In order for the FDA to approve the device for clinical trials, the calves needed to live for at least one month. Cohn and Frazier’s device trumped these standards, with many calves living healthily for full 90-day studies.
Cohn and Frazier were encouraged, and in March 2011, put their artificial heart into a human patient.
Craig Lewis, 55, was admitted to the Texas Heart Institute with amyloidosis, a rare autoimmune disease that fills internal organs with a viscous protein that causes rapid heart, kidney and liver failure. Without some intervention, Lewis would have been dead in days. Frazier and Cohn decided it was the right moment to test their device and the surgeons undertook the lengthy procedure.
Less than 48 hours later, Lewis was sitting up, talking and using his laptop. When doctors put the stethoscope to Lewis’s heart, all they heard was a steady whir of what sounded like a boat propeller. Lewis survived for six weeks until his failing kidneys and liver got the best of him and his family asked doctors to unplug the device.
Source: CNN







 Federal health officials say the pain reliever in Aleve may be safer on the heart than other popular anti-inflammatory drugs taken by millions of Americans.
Federal health officials say the pain reliever in Aleve may be safer on the heart than other popular anti-inflammatory drugs taken by millions of Americans.