1. Reduce Sun Exposure
Especially between 11 am and 4 pm, when the sun’s UV rays are the strongest or when UV index is 3 or more.
2. Shade your Skin
- Seek shade under trees, or create your own shade with a hat, shirt, or umbrella.
- Wear clothing to cover your arms and legs. Make sure the fabric has a tight weave. Fabric that is wet or has a loose weave will allow more light to penetrate through to the skin.
- Wear a wide brimmed hat and sunglasses with UV protection.
3. Beware of clouds
Up to 80% of the sun’s rays can penetrate light clouds, mist and fog. You can still get a sunburn on a cloudy day.
4. Remember about Reflection
Water, sand, snow and concrete can reflect up to 80% of the sun’s damaging rays.
5. Slop on the Sunscreen
Use sunscreens with an SPF of 15 or more that contain both UVA and UVB protection.
Apply sunscreen 15-30 minutes before going outside, and reapply every 2 hours (more often when working, playing, or swimming).
6. Avoid tanning salons and sunlamps
These lights emit mostly UVA radiation – up to 2 – 5 times as much as natural sunlight. UVA radiation causes sunburn, premature aging of the skin and skin cancer.
The UVB radiation from tanning lights is the main cause of sunburn and skin cancer and also contributes to premature skin aging.
For more information see youth tanning (link to being modified by the school team)
7. Protect Children
The most harmful effects of sun exposure occur during early childhood. Keep babies under 1 year out of direct sunlight. Once infants turn 6 months of age, begin using a sunscreen for added protection. It’s important to protect your child’s eyes by using plastic lens sunglasses that protect against UVA and UVB rays.
- Children should have arms and legs covered when out in the sun.
- Instead of wearing baseball caps, they should wear hats with a wide brim, which provides more sun protection.
- When children are playing in the water, make sure to use waterproof sunscreen.
8. Protect your Eyes
Radiation from the sun can damage cells in the structures of your eyes. UV radiation from the sun may increase the risk of developing cataracts later in life. UV radiation can also contribute to the development of skin cancer on the eyelid or on the surface of the eye. This damage can be prevented by protecting your eyes with sunglasses that protect against 100% UVA and UVB rays. Wearing a hat with a wide brim all the way around when out in the sun. Legionnaire style caps (caps with a flap a back flap) are also recommended to help protect the neck, ears and face.
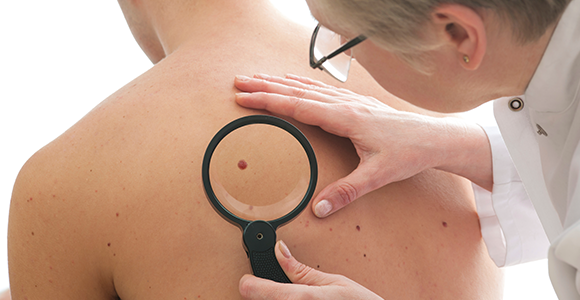
9. Spot Check Your Moles
- Examine your moles and freckles every month to check for any changes. See your health care provider immediately if you notice:
- a mole or discolouration that appears suddenly or begins to change
- a sore that does not heal
- areas of skin that are red and bumpy, bleed or are itchy
Source: health unit