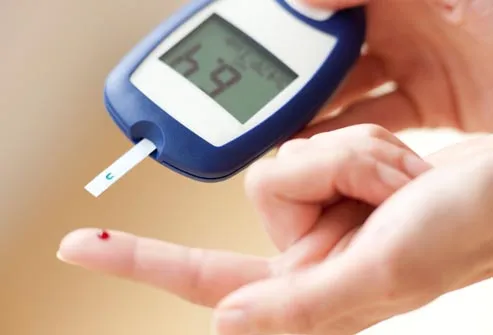
Diabetes is a lifelong medical condition that makes people resistant to insulin, a hormone that allows blood glucose to enter the body’s cells where it is used as energy.
Diabetics have too much glucose in the blood because the body cannot use it properly and they need extra insulin to allow their cells to take in sugar from their blood.
Diabetes has three distinct classifications. These include Type 1 Diabetes wherein a glitch in immune system attacks its own beta cells in the pancreas. A person with type 1 diabetics is dependent on insulin shots for life.
Type 2 Diabetes is triggered by reduced insulin sensitivity combined with reduced insulin secretions. As the disease progresses therapeutic replacement of insulin becomes necessary. The third, gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancies and is fully treatable but requires careful medical supervision throughout pregnancy.
What causes diabetes?
According to experts, nature as well as nurture play a vital role in triggering diabetes. Though, the ailment is said to be passed down from parents to offspring, the gene susceptibility is just 25 percent. A sedentary lifestyle, adhering to unhealthy diet high in saturated fats and junk food, makes us more vulnerable to the ailment.
If diabetes goes uncontrolled it can lead to loss of eye sight, renal failure, cardiovascular problems, gangrene, and amputations, hence maintaining blood sugars within the target range is crucial.
Tips to control diabetes
Though not many can control diabetes without medication, awareness of what makes your blood sugar spike, plus a few simple lifestyle changes can make a real difference.
Diet
In terms of food intake, what you eat, how much you eat and when you eat is paramount for diabetes management. Switch to vegetables and fruits, whole grains, lean meats, or proteins and avoid heavy, processed or refined foods and sweets. Eat five to six small portions throughout the day at a regular time rather than when you feel like it. Balance out all the nutrients in every meal as this will help you keep your insulin level on an even keel.
Regular exercise regimen
Diabetes need to adhere to a regular exercise regimen. Physical activity not only increases insulin sensitivity, but it reduces stress, improves blood pressure and cholesterol and also controls weight. Aim to exercise at least 30 minutes a day, five times a week. Any activity ranging from brisk walking, using stairs instead of elevators, vacuuming that raises metabolic rate and levels out blood sugar counts toward your daily total.
Keeping weight in check
Being overweight is an indicator of diabetes. Excess body fat, especially stored around the abdomen, can increase the body’s resistance to the hormone insulin. Though shedding pounds and keeping it off is a challenging task, losing even a relatively small amount of weight can go a long way in keeping blood sugars levels steady.
Eyes
Visit an ophthalmologist experienced in treating diabetic to look for diseases such as retinopathy, one of the most common complications of the disease.
Quit smoking
Smokers are twice as likely to develop diabetes as opposed to non-smokers. Lighting up reportedly increases insulin resistance and also narrows blood vessels which in turn limit circulation to your legs and feet.
Drink moderately
Excessive alcohol consumption can pile on the pounds and also spike blood pressure and triglyceride levels. Two standard drinks a day for men and no more than one for women is recommended
Get enough sleep
Adjust the hours so that you get a consistent eight hours of shut eye. Researches have established that inadequate sleep has a significant effect on your blood sugar and insulin levels.
Stay hydrated.
Drink water to stay energized and hydrated. Swapping coffee, soda or juices with water will slash the total sugar and calories in your diet. You can add a dash of lemon or lime or an orange wedge for flavor.
Diabetes is serious, but is a manageable disease. Just incorporate these simple tips to prevent or delay some of the serious problems related with diabetes.
Source: the med guru

